Blockchain Smart Contract Basics: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding the Technology
Introduction to Blockchain Smart Contracts
Did you know that over 60% of enterprises are exploring the potential of blockchain technology for smart contracts? As a decentralized digital agreement, smart contracts enable automated execution, which eliminates the need for intermediaries. This means simpler and quicker transactions in various fields, from finance to real estate.
What Are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. For example, imagine a vending machine: you insert money, select a product, and the machine delivers it automatically. Similarly, smart contracts run on blockchain technology, ensuring transparency and security. So, how does this differ from traditional contracts?
Key Differences Between Traditional and Smart Contracts
- Automation: Smart contracts execute automatically once conditions are met, while traditional contracts require manual execution.
- Security: Being hosted on a decentralized blockchain, smart contracts are less prone to fraud or manipulation compared to their traditional counterparts.
- Cost-Effective: Eliminating intermediaries reduces expenses tied to contract enforcement.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Let’s break it down with a straightforward example: suppose two people, Alice and Bob, want to exchange digital assets. A smart contract is a program they deploy, which performs the swapping once both parties confirm the terms. Here’s a simplified view of the process:
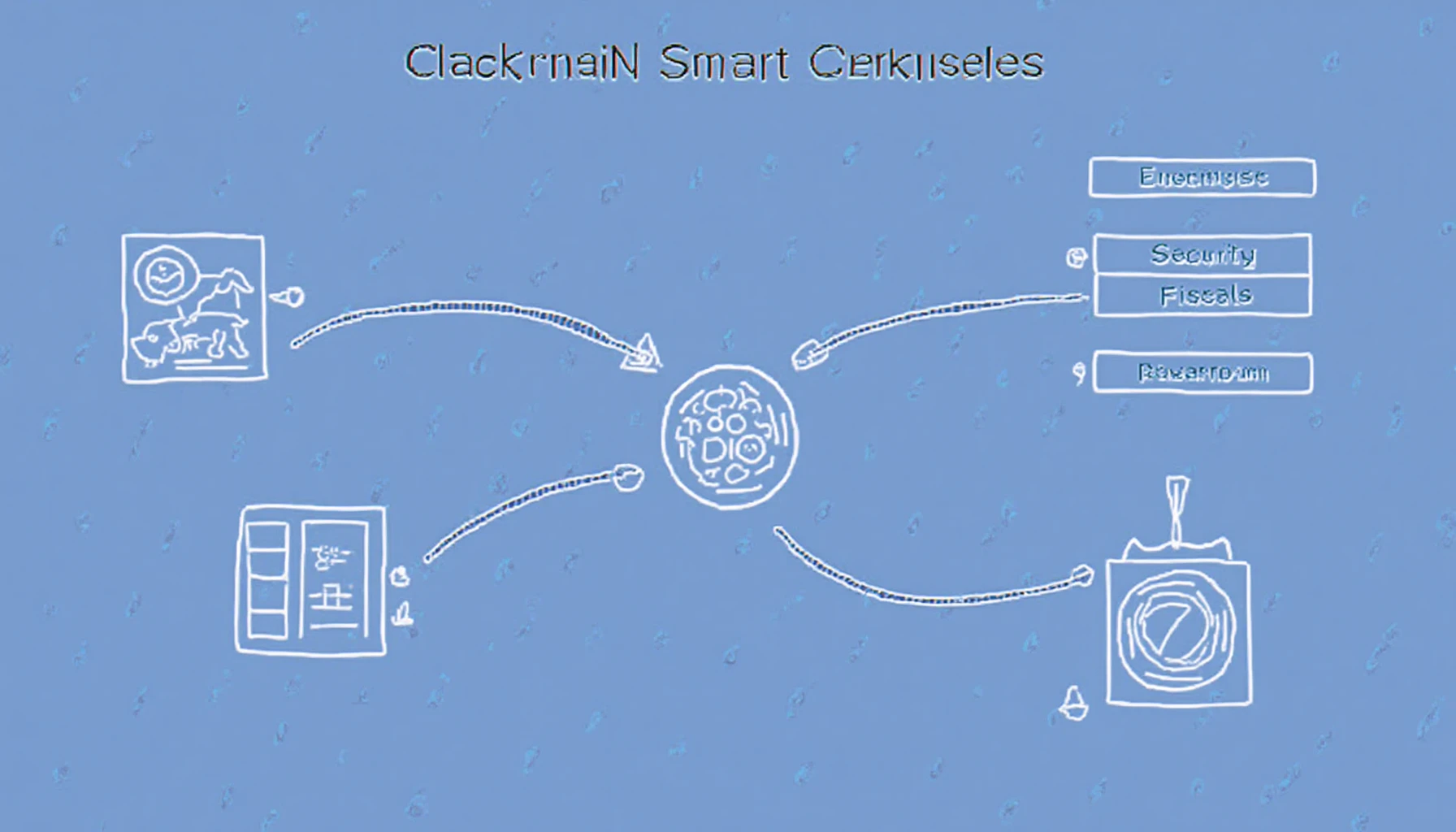
- Agreement Creation: Both parties agree on the conditions.
- Deployment: The smart contract is deployed onto the blockchain.
- Execution: Once conditions are satisfied, the contract executes automatically.
- Completion: The results are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Finance: Automated loan disbursements and trade settlements.
- Real Estate: Streamlined property transfers through title registration.
- Supply Chain: Improved tracking and accountability from inception to delivery.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In summary, blockchain smart contracts represent a groundbreaking approach to digital transactions, offering transparency, security, and efficiency. If you’re considering utilizing this technology, make sure to assess potential platforms and stay informed on regulations in your area, such as the Singapore cryptocurrency tax guide for compliance. Interested in diving deeper? Download our free security wallet guide today to protect your digital assets!