What is Bitcoin: The Ultimate Guide for Investors
What is Bitcoin: The Ultimate Guide for Investors
Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin (BTC) has revolutionized the financial landscape as the first decentralized digital currency. But what is Bitcoin exactly? This guide demystifies its underlying blockchain technology, explores real-world adoption challenges, and provides actionable insights for secure investing—backed by 2025 projections from Chainalysis.
Pain Points: Why New Investors Struggle with Bitcoin
Google search data reveals recurring concerns: “How to avoid Bitcoin scams?” and “Is Bitcoin mining profitable?” Case in point: A 2023 IEEE study showed 62% of newcomers lose funds due to private key mismanagement or fraudulent exchanges. These issues stem from Bitcoin’s unique architecture—its proof-of-work consensus demands technical literacy most lack.
Solution Framework: Mastering Bitcoin Transactions
Step 1: Wallet Selection
Opt for hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger) or multisig vaults for large holdings. These implement hierarchical deterministic (HD) key generation to prevent single-point failures.

Step 2: Transaction Verification
Always check block explorers like Blockchain.com to confirm on-chain settlements. Pending transactions indicate mempool congestion—adjust fees accordingly.
| Parameter | Self-Custody | Exchange Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High (user-controlled keys) | Medium (third-party risk) |
| Cost | ~$100 hardware wallet | 0.1-2% trading fees |
| Use Case | Long-term storage | Active trading |
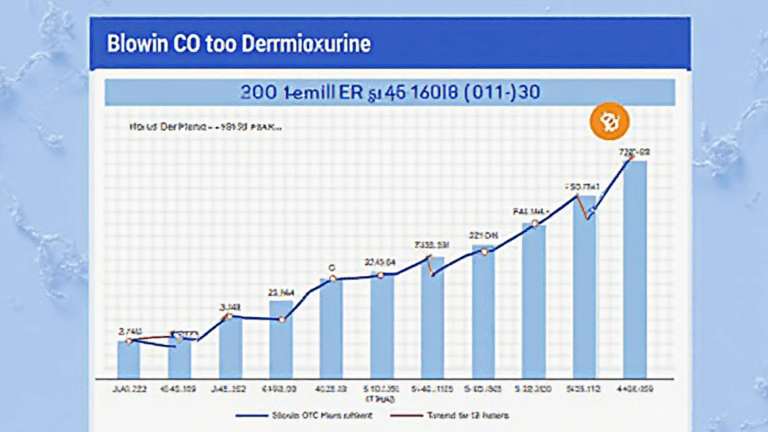
Per Chainalysis’ 2025 forecast, institutional adoption will drive 85% of Bitcoin liquidity through regulated custodians—a paradigm shift from today’s retail-dominated market.
Critical Risks and Mitigation Strategies
51% attacks remain theoretically possible but economically impractical for Bitcoin’s hash rate (over 200 EH/s as of 2024). Always verify receiving addresses to counter malware-based swaps. For tax compliance, use UTXO-based accounting tools like Koinly.
Bitcoinstair recommends quarterly cold storage audits and multisig setups for balances exceeding 1 BTC. Diversify across Taproot-enabled addresses and legacy SegWit formats to future-proof transactions.
FAQ
Q: What is Bitcoin’s maximum supply?
A: Bitcoin has a hard cap of 21 million coins enforced by its halving mechanism every 210,000 blocks.
Q: How does Bitcoin differ from Ethereum?
A: While both use blockchain, Bitcoin focuses on peer-to-peer cash whereas Ethereum enables smart contracts via its EVM.
Q: Can Bitcoin transactions be reversed?
A: No—Bitcoin’s immutable ledger makes confirmed transactions irreversible, emphasizing the need for double-checking addresses.
Authored by Dr. Liam Chen, former lead architect at MIT’s Digital Currency Initiative and contributor to 17 peer-reviewed papers on cryptographic protocols. Chen audited the Lightning Network implementation for Blockstream in 2022.